Vue Loader
Vue Loader 是一个 webpack 的 loader,它允许以一种名为单文件组件 (SFCs)的格式撰写 Vue 组件。本文将探究 .vue 文件中template、script、style及自定义块是如何解析为 Vue 组件对象,并在浏览器端运行。
Webpack
众所周知,现代前端工程化离不开webpack,从本质上来说,webpack 是一个现代 JavaScript 应用程序的静态模块打包器。
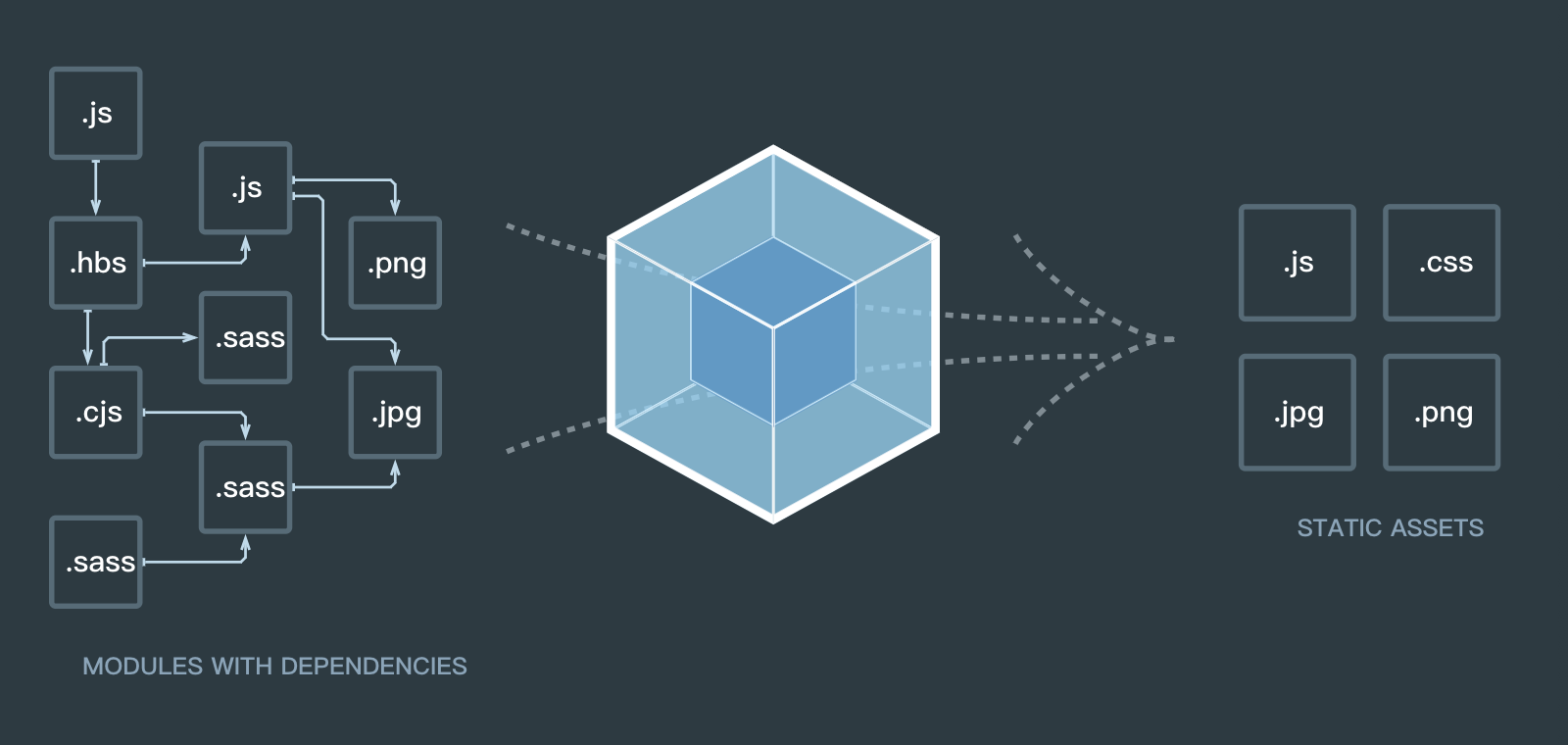
.vue 文件的解析及运行同样离不开webpack,下面将从vue-loader的loader与plugin两个方面来解析vue单文件组件系统的实现过程。
需要值得注意的是,本文档基于webpack4.0+版本来解读vue-loader。webpack4.0+版本基于原有版本进行大幅度升级,原有webpack拆分为webpack、webpack-dev-server、webpack-cli三个npm包,配置层面也更加倾向于零配置,当然loader与plugin的api层面也有变化
Loader
首先,webpack的loader到底是什么?
官方文档中这么进行解读的:所谓 loader 只是一个导出为函数的 JavaScript 模块。
下面我们来看一下最简单的loader实现:
- 配置package.json
"scripts": {
"serve": "webpack-dev-server --config example/webpack.config.js --inline --hot"
}
- 配置webpack.config.js
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: path.resolve(__dirname, './main.damo'),
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js',
publicPath: '/dist/'
},
devServer: {
contentBase: __dirname
},
module: {
rules:[
{
test: /\.damo$/,
loader: 'test-loader'
}
]
},
resolveLoader: {
alias: {
'test-loader': require.resolve('../lib')
}
}
}
- 配置loader
module.exports = function (source) {
let code = `
let style = document.createElement("style");
style.innerText = ${JSON.stringify(source)};
document.head.appendChild(style);
`
return code;
}
从上述案例中可以看出,loader 接受 source 并返回 code 。而source 便是 .damo 文件中字符串化的代码,code 是对 source 加工处理后的字符串。为此,大致上可以认为,loader 接受 String 并返回 String。
vue-loader 也是类似的机制,不同于简单的loader,它利用 VueLoaderPlugin 插件解析了 .vue 文件中的template 、style 、script 三个模块,并把各模块解析后的代码利用 vue 组件生成函数构建为组件导出,从来实现了在浏览器端运行 .vue 文件的功能。代码如下:
//templateImport、scriptImport、stylesCode分别为 .vue 文件中各模块导出的js代码
let code = `
${templateImport}
${scriptImport}
${stylesCode}
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from ${stringifyRequest(`!${componentNormalizerPath}`)}
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
${hasFunctional ? `true` : `false`},
${/injectStyles/.test(stylesCode) ? `injectStyles` : `null`},
${hasScoped ? JSON.stringify(id) : `null`},
${isServer ? JSON.stringify(hash(request)) : `null`}
${isShadow ? `,true` : ``}
)
`.trim() + `\n`
code += `\nexport default component.exports`
vue-loader 的 loader 模块并没有实现解析 .vue 文件中的template 、style 、script 三个模块的功能,解析过程是通过其 plugin模块 来实现的
Plugin
官方文档中这么进行解读的:插件是 webpack 生态系统的重要组成部分,为社区用户提供了一种强大方式来直接触及 webpack 的编译过程。插件能够钩入到在每个编译中触发的所有关键事件。
下面演示了一个简单 plugin 引入的大致过程:
- 配置webpack.config.js
const TestLoaderPlugin = require('../lib/plugin')
module.exports = {
// ... 这里是其他配置 ...
plugins:[
new TestLoaderPlugin(
()=>{
console.log('run')
},
()=>{
console.log('failed')
}
)
]
}
- 配置plugin
class TestLoaderPlugin {
constructor(doneCb,failCb){
this.doneCb = doneCb;
this.failCb = failCb;
}
//webpack 初次加载完此插件后执行,只会在 webpack 启动的时候被执行一次
apply(compiler){
compiler.hooks.done.tap('TestLoaderPlugin', (compiler) => {
this.doneCb();
});
compiler.hooks.failed.tap('TestLoaderPlugin', (compiler) => {
this.failCb();
});
}
}
module.exports = TestLoaderPlugin
倘若开发一个简单loader,并不需要引入 plugin。当需要解析特定结构下的单文件时,因 loader 不能触及 webpack 编译过程的特性,plugin 将不可或缺。
通常来说,plugin 是 webpack 的核心功能,用于解决 loader 无法实现的事,包括但不限于 改写 loader 解析的 rule 、触发 compiler 编译器相关的 hook 、 触发compilation 编译过程中的 hook等。
在 vue-loader 中, VueLoaderPlugin 插件主要承担了三项职责:
1. 改写 webpack 中的 module.rule
2. 通过 pitch 函数拦截并转换 .vue 文件的 template、script、style 及 custom 模块的请求
3. 调用相应的模块编译器对各模块的请求进行编译
代码如下:
//@vue/component-compiler-utils
//compileTemplate
const templateLoaderPath = require.resolve('./templateLoader')
//compileStyle
const stylePostLoaderPath = require.resolve('./stylePostLoader')
const isCSSLoader = l => /(\/|\\|@)css-loader/.test(l.path)
//pitch loader
module.exports.pitch = function (remainingRequest) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const query = qs.parse(this.resourceQuery.slice(1))
let loaders = this.loaders
const genRequest = loaders => {
const seen = new Map()
const loaderStrings = []
loaders.forEach(loader => {
const identifier = typeof loader === 'string'
? loader
: (loader.path + loader.query)
const request = typeof loader === 'string'
? loader
: loader.request
if (!seen.has(identifier)) {
seen.set(identifier, true)
loaderStrings.push(request)
}
})
return loaderUtils.stringifyRequest(this, '-!' + [
...loaderStrings,
this.resourcePath + this.resourceQuery
].join('!'))
}
if (query.type === `style`) {
const cssLoaderIndex = loaders.findIndex(isCSSLoader)
if (cssLoaderIndex > -1) {
const afterLoaders = loaders.slice(0, cssLoaderIndex + 1)
const beforeLoaders = loaders.slice(cssLoaderIndex + 1)
const request = genRequest([
...afterLoaders,
stylePostLoaderPath,
...beforeLoaders
])
return `
import mod from ${request};
export default mod;
export * from ${request}`
}
}
if (query.type === `template`) {
const path = require('path')
const request = genRequest([
templateLoaderPath + `??vue-loader-options`,
...loaders
])
return `export * from ${request}`
}
if (query.type === `custom` &&
loaders.length === 1 &&
loaders[0].path === selfPath) {
return ``
}
const request = genRequest(loaders)
return `
import mod from ${request};
export default mod;
export * from ${request}`
}
//stylePostLoader
const qs = require('querystring')
const { compileStyle } = require('@vue/component-compiler-utils')
module.exports = function (source, inMap) {
const query = qs.parse(this.resourceQuery.slice(1))
const { code, map, errors } = compileStyle({
source,
filename: this.resourcePath,
id: `data-v-${query.id}`,
map: inMap,
scoped: !!query.scoped,
trim: true
})
if (errors.length) {
this.callback(errors[0])
} else {
this.callback(null, code, map)
}
}
//templateLoader类似,详情可查阅下方源码解析
Flow
vue-loader的流程图大体如下:

附录
个人源码分析版本地址: damo-loader